CBCT Tomography is a three-dimensional imaging technology, which has been specifically developed for imaging of the teeth and jaws. It has an applications in implant dentistry, endodontics and oral surgery.
CBCT provides three-dimensional imaging and has been used to overcome the inherent problems with conventional two-dimensional radiographic techniques
CBCT is a low dose scanning system, which has been specifically designed to produce three-dimensional images of the maxillofacial skeleton CBCT scanners use back-projection reconstructed tomography to acquire data of the area of interest through a single or partial rotation of the conical X-ray beam and reciprocal image receptor
As the patient is stationary and the motion of the gantry is a simple rotation, the main complexity of the CBCT system lies in the detector and the data processing technology.
Advantage of CBCT
1.Better image quality and accuracy
The 3D capabilities mean that the dentist can view what’s going on in the patient’s mouth from different angles for better diagnosis and a complete evaluation.
3.Images bone and soft tissues
This scan provides more information than a conventional dental X-ray, allowing the dentist to create a more precise treatment plan.
4.A lower dose of radiation
The CBCT scan uses a lower dose of radiation than a regular CT scan.
5.Quick and painless
In dentistry, x-rays are divided into two main categories, intraoral and extraoral.
Intraoral Radiographs (film is inside the mouth.)
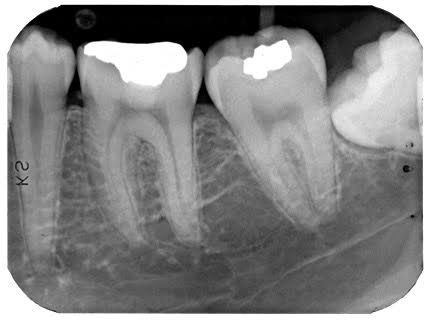
Intraoral X-rays are the most common type. They give a high level of detail. These X-rays allow dentists to:
- Find cavities
- Look at the tooth roots
- Check the health of the bony area around the tooth
- See the status of developing teeth
- Otherwise monitor good tooth health
The various types of intraoral X-rays show different aspects of the teeth:
Bite-wing X-rays
One or two bite-wing X-rays on each side of the mouth are taken. Each X-ray shows the upper and lower molars (back teeth) and bicuspids (teeth in front of the molars). These X-rays help dentists find decay between back teeth.
Periapical X-rays
This shows the entire length of each tooth, from crown to root. This highlight only one or two teeth at a time.
Occlusal X-rays
This is larger than most X-rays. They highlight tooth development and placement in children. Each X-ray shows nearly the full arch of teeth in either
Extraoral Radiographs (film is outside the mouth)
This can be considered the “big picture” X-rays. They show teeth, but they also provide information on the jaw and skull. Extraoral radiographs are used to:
- Keep track of growth and development
- Look at the status of impacted teeth
- Examine the relationships between teeth and jaws
- Examine the bones of the face
The various type of extraoral X-rays
1.Panoramic X-rays show the entire mouth on a single X-ray. They include all teeth on both upper and lower jaws.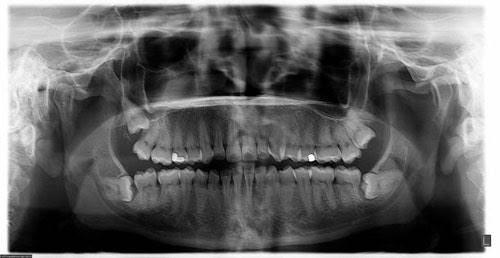
2.Cephalometric projections are X-rays taken of the entire side of the head. They are used to look at the teeth in relation to the jaw and the person’s profile. Orthodontists use cephalometric projections to determine the best type of orthodontic treatment.
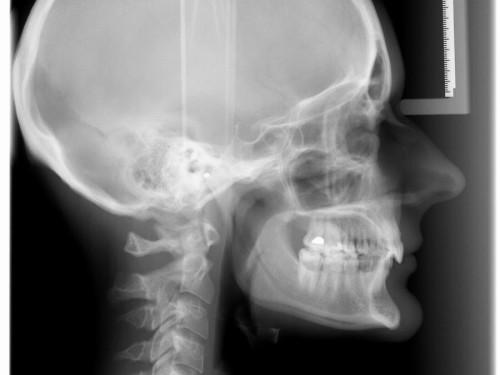
3.Cone-beam computed tomography (CT) provides three-dimensional images. A cone-beam scan uses less radiation than a medical CT scan but far more than any standard dental X-ray. The cone-beam CT is particularly useful for dental implant selection and placement.